Final tests for the LHCf detector
LHCf is the LHC experiment dedicated to measuring neutral particles such as gamma-rays or neutrons at the very forward region of LHC IP1, in order to verify hadronic interactions of ultra-high energy cosmic rays.
The experiment consists of two compact detectors, Arm1 and Arm2, having a pair of small tungsten sandwich calorimeters with position sensitive layers. The key characteristic of the detector is determining the energy and incident position reconstruction of ~TeV showers with a very compact calorimeter.
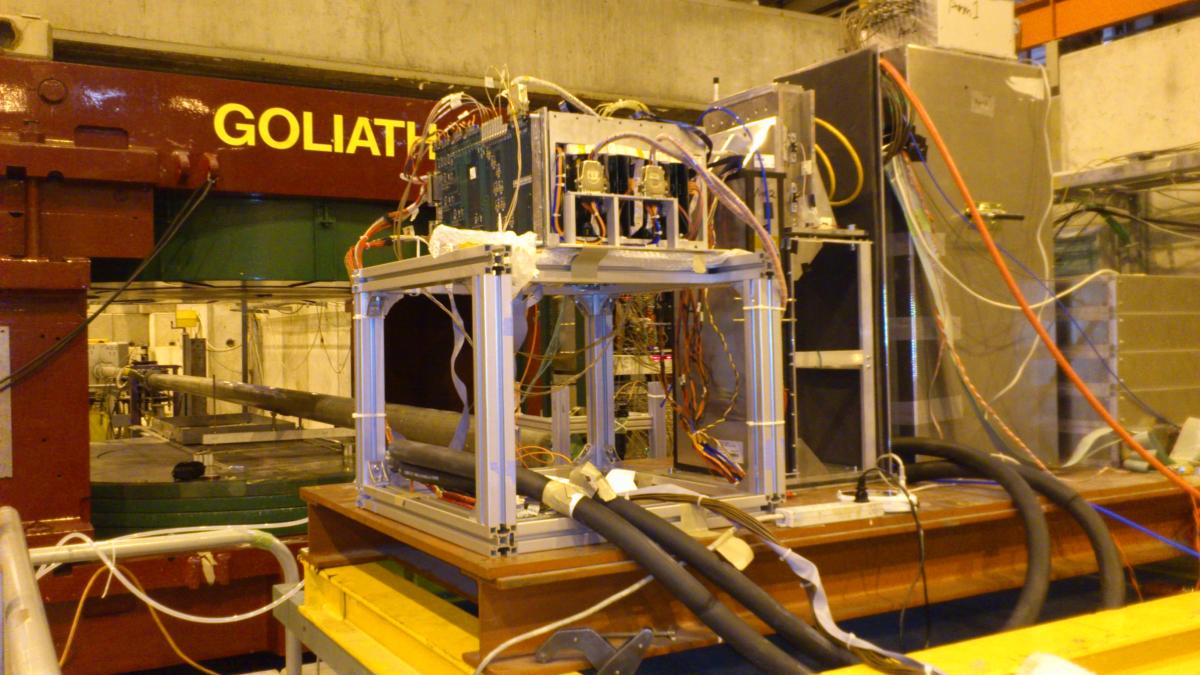

The original detector used in previous LHC 7 TeV p-p and p-Pb runs has been upgraded by replacing plastic scintillator layers and scintillating fibers by GSO scintillators and 1mm pitch GSO hodoscopes, respectively. They must be installed between two LHC beam pipes this November, therefore this October has been the only chance for an SPS beam test to confirm the real performance of the new detectors.
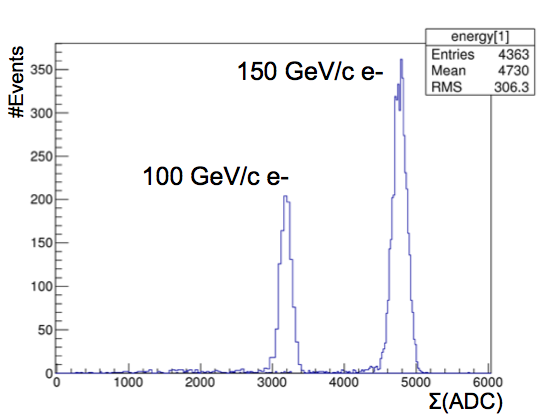
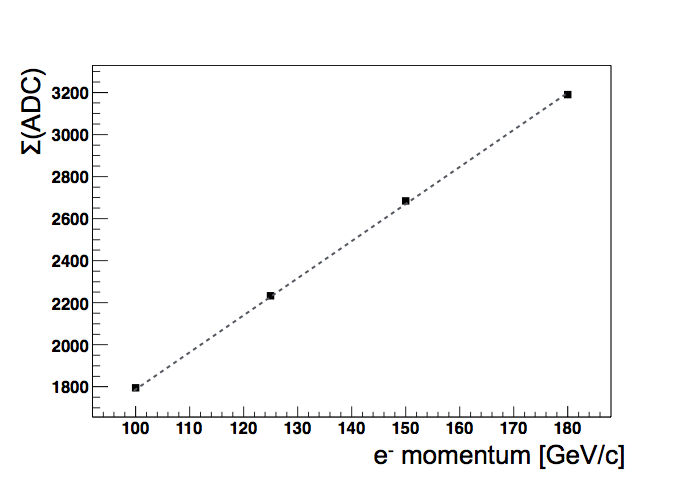
The plots show the ADC distribution for each beam energy and the response linearity ( ADC vs beam energy )
The beam test was performed from 6 to 16 October at H4 with subsequent beams of 100-180GeV/c electrons, 300 GeV/c protons and 150 GeV/c muons. The new detector has successfully shown good performance as designed, and is now ready for installation.
