SME
MUonE: A new path to hadronic vacuum polarization and the running of α
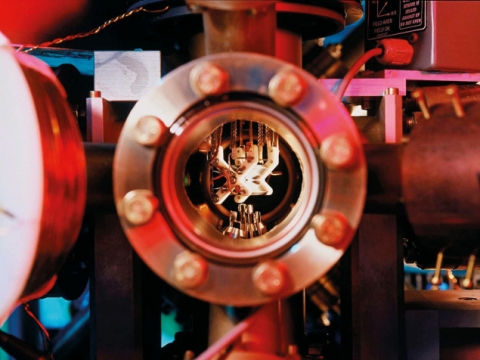
Promising results Promising results - A test run for the proposed MUonE experiment took place at CERN in the summer. The image shows a 20 mm thick graphite scattering target (left) and a silicon strip tracking module (right). Credit:…
Read moreSympathetic Cooling Opens a New Era for Antihydrogen at CERN
A major milestone has been reached at CERN’s Antimatter Factory. Using an innovative technique to cool positrons with laser-cooled beryllium ions, the ALPHA collaboration has increased the rate of antihydrogen production by a factor of eight. The…
Read moreQuantum Science and Technologies and High-Energy Physics
Trapped ions: A quantum simulator at the University of Innsbruck. Credit: C Lackner/Innsbruck On 27–28 October 2025, CERN hosted the Symposium on Quantum Science and Technologies and High-Energy Physics (HEP), co-organised through the CERN Quantum…
Read moreAMBER — En route to measure the proton radius
After months of excitement and almost continuous, frenetic activity since August, AMBER’s vast experimental hall — more than 10 m high and stretching over 60 m from the upstream collimators to the far wall — now feels unusually quiet and solitary.…
Read moreTransfer-induced fission at the ISOLDE Solenoidal Spectrometer
How are the heaviest elements in the Universe formed? Looking at the periodic table, we know where the lightest elements come from. Hydrogen and helium were forged in the primordial nucleosynthesis that took place just moments after the Big Bang.…
Read moreMarek Gazdzicki: Four Decades at the SPS – and Still Surprised by Strong Interactions
After nearly two decades at the helm of NA61/SHINE, Marek Gazdzicki reflects in this interview on a lifetime at the SPS — from proposing the world’s first two-dimensional scan of nuclear collisions to the unexpected discovery of a large isospin…
Read moreISOLDE charts the shores of the islands of inversion
For decades, CERN’s ISOLDE (Isotope Separator On-Line Device) facility has been a global leader in exploring the behaviour of exotic nuclei far from stability. By delivering beams of short-lived isotopes and enabling their study with advanced…
Read moreBreakthrough: Coherent Spectroscopy with a Single Antiproton Spin
BASE physicist Barbara Latacz in front of the experiment’s cryostat. This cylinder, which is kept at 4 kelvins (-269°C), houses the system of traps that cool and measure the antiprotons and a very strong magnet. (Image: CERN) In a significant…
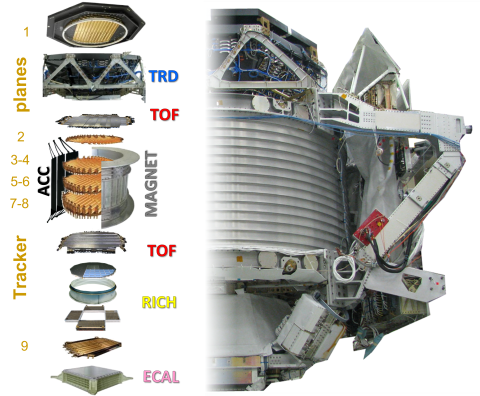
Read moreAMS-02: A New Chapter in Orbit to Probe the Nature of Cosmic Rays
Since its launch aboard the International Space Station (ISS) in May 2011, the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS-02) has recorded more than 250 billion cosmic-ray events, offering precision measurements of the composition and energy spectra of…
Read moreDecoding r-Process Nucleosynthesis: Precision Studies of Exotic Indium Isotopes at ISOLDE
How are the chemical elements synthesised in stellar environments? Which processes lead to their creation? What impact does nuclear physics have on their production? Describing the origins of the chemical elements and their observed…
Read more