SME
SHiP collaboration sets course on New Physics
The Search for Hidden Particles (SHiP) experiment with the associated Beam Dump Facility (BDF), currently under consideration for implementation in the SPS ECN3 beam facility, is designed to perform a generic and exhaustive search for feebly…
Read moreISOLDE lays the ground for CP violation tests with radioactive molecules
All atoms heavier than bismuth, which has 83 protons, are radioactive and their isotopes have short half-lives, with few exceptions. As a result, the study of heavy atoms and their molecular compounds is complicated by the radioactive decay of the…
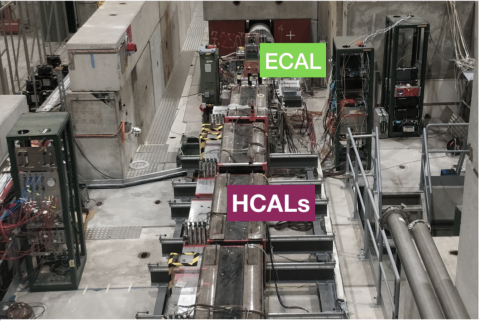
Read moreFirst Physics Results from the FASER Experiment
FASER is a new small LHC experiment designed to search for light, weakly interacting, long-lived beyond-standard model particles such as dark photons and to detect high energy neutrinos produced in proton-proton collisions. The FASER detector is…
Read moreANUBIS: a guide into the dark sector
The ancient Egyptians believed Anubis was a jackal-headed god who accompanied kings to the underworld. Today we know better: ANUBIS is a proposed extension to the ATLAS detector to explore the dark sector by searching for long-lived particles (LLPs…
Read moreLighting the dark with NA64: news from Light Dark Matter searches
The existence of Dark Matter (DM) has been inferred by Cosmology and Astrophysics through its gravitational effects. However, its microscopic nature remains one of the most pressing questions in particle physics. Scenarios in which the DM is a…
Read moreChronicles of SND@LHC’s first year of data taking
The year 2022 saw the culmination of 18 months of intense preparatory work with the SND@LHC Collaboration entering the highly anticipated phase of commissioning with beam and first year of data taking. After the installation of the neutron shield…
Read moreRadioactive ion beams at ISOLDE bring the nuclear clock a tick closer
The precise measurement of time and frequencies has always played an important role in the history of science. Since the adoption of the caesium-133 standard as the definition of the second within the Système International (SI) in 1967, a network of…
Read moreHIKE collaboration targets a new era of kaon experiments
The recently proposed High Intensity Kaon Experiments (HIKE) project offers a long-term vision for a research programme at CERN, covering experimental searches in the kaon sector that could enable a new generation of searches and indirectly probe…
Read moreMILLIQAN gets ready to have a look at the dark
The milliQan collaboration is on track to finish the installation and commissioning of their Run 3 detector before the end of the YETS, Components of both the “bar” and “slab” detectors have been placed in a tunnel above the CMS experimental cavern…
Read moreThe birth of NanoCal
High-performance electromagnetic calorimeters often make use of inorganic crystal scintillators. Their high density makes them well suited for the construction of large homogeneous detectors where the scintillating material simultaneously serves as…
Read more