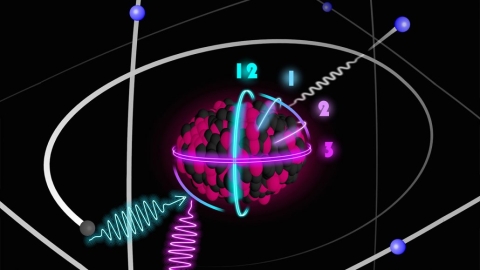
ISOLDE
Decoding r-Process Nucleosynthesis: Precision Studies of Exotic Indium Isotopes at ISOLDE
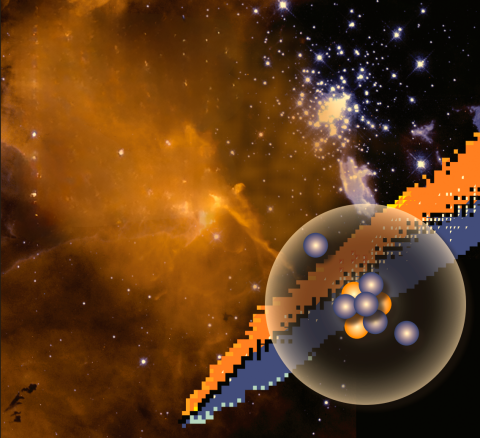
How are the chemical elements synthesised in stellar environments? Which processes lead to their creation? What impact does nuclear physics have on their production? Describing the origins of the chemical elements and their observed…
Read moreUpdates from the ISOLDE Solenoidal Spectrometer
The field of nuclear physics is well into its second century. From its initial experiment bombarding a gold foil with alpha particles, experimental techniques have become more sophisticated to keep pace with the technology and innovation that has…
Read morePerturbed angular correlations at ISOLDE
Solid state physics and biophysics research has been conducted at ISOLDE-CERN for almost 50 years [JOH2017]. Our role in supporting experimental equipment and manpower has enabled the development of on-site laboratories. This has several advantages…
Read moreInvestigating exotic structures of exotic nuclei with Miniball
Atomic nuclei come in all manner of shapes and sizes, sometimes at the same time! The reason behind this diversity lies in poorly understood nuclear forces. Many features of these forces only came to light when studying very unstable nuclei, which…
Read moreRadioactive ion beams at ISOLDE bring the nuclear clock a tick closer
The precise measurement of time and frequencies has always played an important role in the history of science. Since the adoption of the caesium-133 standard as the definition of the second within the Système International (SI) in 1967, a network of…
Read moreThe LISA project at CERN-ISOLDE
The LISA (Laser Ionisation and Spectroscopy of Actinides) consortium aims to train a new generation of experts in radioactive ion beam research and applications, laser spectroscopy, scientific laser…
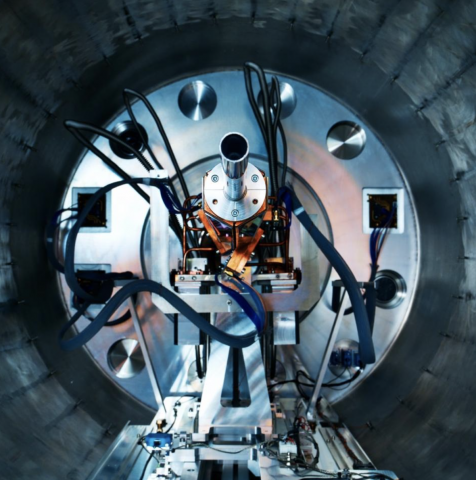
Read moreISOLDE's Solenoidal Spectrometer (ISS): a new tool for studying exotic nuclei
The majority of atomic nuclei exist away from the valley of beta-stability, so it is perhaps unsurprising that in studying them nuclear physicists have discovered emerging phenomena not seen in stable nuclei. Changing shell structure, evolving…
Read moreThe many faces of ISOLDE
You will stand across the street from the ISOLDE facility, when visiting CERN’s medical center, fire fighters, raw materials store, transport teams, or goods reception service. Located centrally at the Meyrin site (https://videos.cern.ch/record/…
Read moreISOLDE determines precise nuclear moments by devising novel experimental technique
Nuclear quadrupole moments (Q), a measure of charge asymmetry in nuclei, are experimentally accessible via the quadrupole interaction frequency νQ=eQVzz/h. To extract Q from this information one needs to know Vzz, the electric-field gradient at the…
Read moreSecrets of beta decay unraveled at ISOLDE
Ernest Rutherford, in 1899, separated radioactive emissions into two types: alpha and beta. Becquerel, in 1900, measured the mass-to-charge ratio of beta particles and identified them as electrons. The theory of β decay was developed by Fermi in…
Read more