CMS
Dark Showers at the LHC: from benchmarks to Run-3 readiness
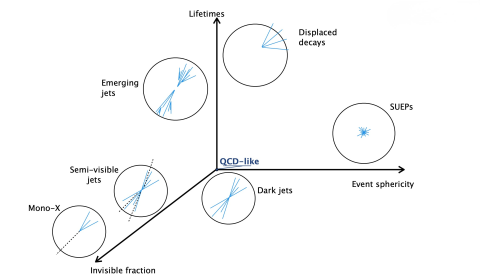
The search for new physics at the LHC increasingly pushes beyond traditional signatures. Among the most intriguing possibilities are dark showers—complex cascades of particles emerging from dark-sector dynamics, capable of producing rich,…
Read moreTriple Higgs Frontiers: Mapping the Higgs self-couplings at the 2025 HHH workshop
More than a decade after the discovery of the Higgs boson, attention is shifting from finding the Higgs to mapping its self-interactions. These self-couplings determine the shape of the Higgs potential, and with it the stability of our vacuum and…
Read moreHighlights from the 2nd NGT Technical Workshop
Participants of the 2nd Next Generation Triggers Technical Workshop at the Globe of Science and Innovation. Picture: Mariana Velho From 19 to 21 November 2025, the Next Generation Triggers (NGT) project held its 2nd Technical Workshop at CERN’s…
Read moreLight ions at the LHC: first results from oxygen–oxygen and neon–neon collisions
This summer, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) delivered its first-ever collisions between light ions, opening a new chapter in the study of nuclear structure and the quark–gluon plasma (QGP) – the extreme state of matter that existed in the first…
Read moreCMS explores light-ion collisions: suppression, scaling, and collectivity
The CMS experiment has reported first results from the LHC’s dedicated oxygen–oxygen (O–O) and neon–neon (Ne–Ne) collision run, offering an unprecedented look at quark–gluon plasma (QGP) formation in light-ion systems. These studies address long-…
Read moreOLC-R / OLC-1 refurbishment in a Nutshell
For Phase-2, CMS DAQ will undergo a major increase of its capacities to match HL-LHC performance and the related CMS physics program. Compared to the present situation (Run3), the post-trigger data throughput will increase from 2 Tb/s today to 50 Tb…
Read moreAn all-round boosted chase for supersymmetry
It is rare for a theory to inspire as much experimental attention as supersymmetry has. CMS completed more than 40 SUSY searches in Run 2 alone, reflecting how compelling this framework remains in the quest for new physics. SUSY proposes that every…
Read moreHow CMS records all 40 million events per second
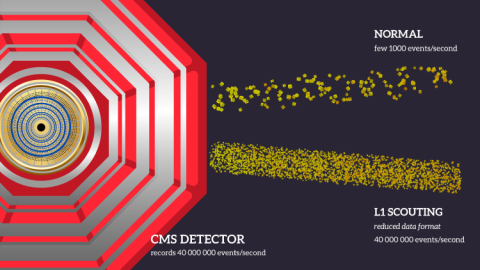
Traditional data taking workflows at the LHC experiments rely on a filtering step – called Level-1 trigger – that reduces the amount of data to a manageable level. The Level-1 trigger is implemented in hardware, takes only a few…
Read moreNext-Generation CO₂ Cooling Systems Powering the Future of ATLAS and CMS
Four CO2 cooling plants and accumulators in the service cavern of CMS in May 2025. (Photo by Jérôme Daguin) During recent shutdown periods, CERN engineers and technicians — in collaboration with the ATLAS and CMS teams — began installing the…
Read moreCMS Inaugurates Its New Control Room
On 15 May 2025, CMS officially inaugurated its new control room at Point 5 in Cessy, France. The celebration brought together guests from CERN management and representatives of all LHC experiments to mark this significant upgrade to CMS’s…
Read more